Case made by Dr.Ahmad Madarati
Patient: Adult patient.
Chief Complaint & Diagnosis: Irreversible pulpitis in tooth #37 (mandibular left second molar).
Pre-operative Assessment: Radiographic examination revealed S-shaped, severely curved, and calcified (obliterated) mesial canals, presenting a high-complexity anatomical challenge.
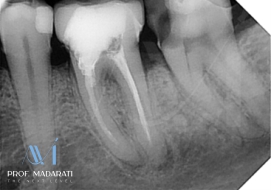
Treatment Procedure:
Access and Initial Negotiation:
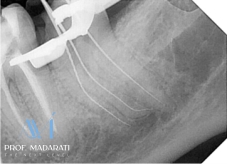
Following access cavity preparation, the two mesial canals were initially scouted using a C-file #8 repeatedly, followed by a K-file #10 to establish patency to the full working length.
Glide Path Preparation:
Given the severe curvature, a dedicated glide path was prepared using rotary path files with a minimal taper (2-3%). Specifically, PA rotary files (Denco Medical) in sizes 13/.02, 16/.02, and 19/.02 were used sequentially to create a safe, smooth pathway.
Cleaning and Shaping:
All canals were then cleaned and shaped using Chameleon Dual Shaper (Denco) in sizes 20/.04 and 25/.04.

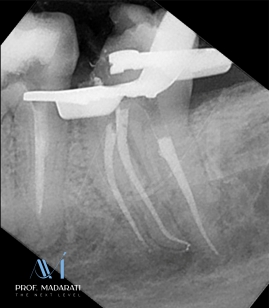
Obturation and Temporary Restoration:
Obturation was performed using the modified warm vertical compaction technique with Maaruchi bioceramic sealer.
A temporary restoration with Glass Ionomer Cement (GIC) was placed. The patient was referred back to the referring dentist for the final restoration.
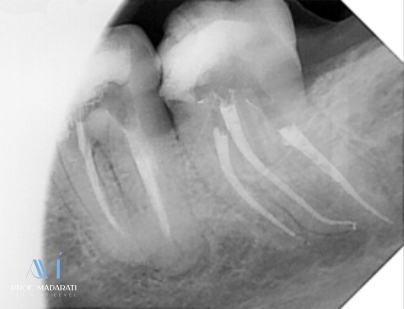
Clinical Significance & Take-Home Message:
This case underscores a critical protocol for high-difficulty anatomy: When managing severely curved and very narrow/calcified canals, it is essential to first prepare a good glide path using dedicated rotary instruments with a small taper (2-3%). This step precedes the use of larger taper shaping files (taper 04 is preferred). This protocol, demonstrated here with PA rotary files for the glide path followed by the Chameleon Dual Shaper for shaping, significantly reduces the risk of procedural errors (such as ledge formation or transportation) and ensures a safe, effective preparation of complex canal anatomy.








